1. numpy(numerical python)
- Python data analysis package for scientific computing
- Provides various useful functionalities necessary for handling multidimensional arrays
- Essential to master along with pandas for data analysis
2. ndarray
- Comprehensive multidimensional array capable of containing data of the same data type
- All elements of the ndarray must use the same data type, and the dimension of the array is called rank, while the size of each dimension is represented as a tuple called shape.
- Example: In a 2-dimensional array with 3 rows and 2 columns, the rank is 3, and the shape is (3,2).
3. Example
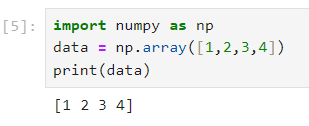
- numpy.array
- numpy.arange(start value, end value, interval) or arange(end value)


- reshape(a, newshape, order='C')
-- Gives a new shape to an array without changing its data.

- numpy. add(data1,data2)
- numpy. subtract(data1,data2)
- numpy.multiply(data1,data2)
- numpy.dot(data1,data2)



| Operation | Description |
| copyto(dst, src[, casting, where]) | Copies values from one array to another, broadcasting as necessary. |
| shape(a) | Return the shape of an array. |
| reshape(a, newshape[, order]) | Gives a new shape to an array without changing its data. |
| ravel(a[, order]) | Return a contiguous flattened array. |
| ndarray.flat | A 1-D iterator over the array. |
| ndarray.flatten([order]) | Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension. |
| moveaxis(a, source, destination) | Move axes of an array to new positions. |
| rollaxis(a, axis[, start]) | Roll the specified axis backwards, until it lies in a given position. |
| swapaxes(a, axis1, axis2) | Interchange two axes of an array. |
| ndarray.T | View of the transposed array. |
| transpose(a[, axes]) | Returns an array with axes transposed. |
| atleast_1d(*arys) | Convert inputs to arrays with at least one dimension. |
| atleast_2d(*arys) | View inputs as arrays with at least two dimensions. |
| atleast_3d(*arys) | View inputs as arrays with at least three dimensions. |
| broadcast | Produce an object that mimics broadcasting. |
| broadcast_to(array, shape[, subok]) | Broadcast an array to a new shape. |
| broadcast_arrays(*args[, subok]) | Broadcast any number of arrays against each other. |
| expand_dims(a, axis) | Expand the shape of an array. |
| squeeze(a[, axis]) | Remove axes of length one from a. |
| asarray(a[, dtype, order, like]) | Convert the input to an array. |
| asanyarray(a[, dtype, order, like]) | Convert the input to an ndarray, but pass ndarray subclasses through. |
| asmatrix(data[, dtype]) | Interpret the input as a matrix. |
| asfarray(a[, dtype]) | Return an array converted to a float type. |
| asfortranarray(a[, dtype]) | Return an array (ndim >= 1) laid out in Fortran order in memory. |
| ascontiguousarray(a[, dtype]) | Return a contiguous array (ndim >= 1) in memory (C order). |
| asarray_chkfinite(a[, dtype, order]) | Convert the input to an array, checking for NaNs or Infs. |
| require(a[, dtype, requirements, like]) | Return an ndarray of the provided type that satisfies requirements. |
| concatenate([axis, out, dtype, casting]) | Join a sequence of arrays along an existing axis. |
| stack(arrays[, axis, out, dtype, casting]) | Join a sequence of arrays along a new axis. |
| block(arrays) | Assemble an nd-array from nested lists of blocks. |
| vstack(tup, *[, dtype, casting]) | Stack arrays in sequence vertically (row wise). |
| hstack(tup, *[, dtype, casting]) | Stack arrays in sequence horizontally (column wise). |
| dstack(tup) | Stack arrays in sequence depth wise (along third axis). |
| column_stack(tup) | Stack 1-D arrays as columns into a 2-D array. |
| row_stack(tup, *[, dtype, casting]) | Stack arrays in sequence vertically (row wise). |
| split(ary, indices_or_sections[, axis]) | Split an array into multiple sub-arrays as views into ary. |
| array_split(ary, indices_or_sections[, axis]) | Split an array into multiple sub-arrays. |
| dsplit(ary, indices_or_sections) | Split array into multiple sub-arrays along the 3rd axis (depth). |
| hsplit(ary, indices_or_sections) | Split an array into multiple sub-arrays horizontally (column-wise). |
| vsplit(ary, indices_or_sections) | Split an array into multiple sub-arrays vertically (row-wise). |
| tile(A, reps) | Construct an array by repeating A the number of times given by reps. |
| repeat(a, repeats[, axis]) | Repeat each element of an array after themselves. |
| delete(arr, obj[, axis]) | Return a new array with sub-arrays along an axis deleted. |
| insert(arr, obj, values[, axis]) | Insert values along the given axis before the given indices. |
| append(arr, values[, axis]) | Append values to the end of an array. |
| resize(a, new_shape) | Return a new array with the specified shape. |
| trim_zeros(filt[, trim]) | Trim the leading and/or trailing zeros from a 1-D array or sequence. |
| unique(ar[, return_index, return_inverse, ...]) | Find the unique elements of an array. |
| flip(m[, axis]) | Reverse the order of elements in an array along the given axis. |
| fliplr(m) | Reverse the order of elements along axis 1 (left/right). |
| flipud(m) | Reverse the order of elements along axis 0 (up/down). |
| roll(a, shift[, axis]) | Roll array elements along a given axis. |
| rot90(m[, k, axes]) | Rotate an array by 90 degrees in the plane specified by axes. |
'Computer > Python & Machine learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4. Pandas (0) | 2024.04.09 |
|---|---|
| 2. Install python packages (0) | 2024.04.05 |
| 1. Install Anaconda (0) | 2024.04.05 |